Launch Details
- Mission Name - TV-D1 / In-Flight Abort Test
- Lift Off - 26 November 2023
- Pad - First Launch Pad, SDSC
- Rocket - Modified L40 Booster
- Payload - Gaganyaan spacecraft and Crew Escape System
- Payload Mass - 12.6 Tons
- Orbit - Suborbital Launch
About the Launch
TV-D1 (Test Vehicle Demonstration) will be a high altitude abort test as part of the Gaganyaan program, set to be held in mid October 2023. With a rocket based upon the GSLV L40 stage, TV-D1, the first development flight from the Gaganyaan program, will be launched up until 11 km from sea level, where an in-flight abort scenario will be initiated, and the capsule should flight until 15-16 km. The mission should test the separation from the rocket and its trajectory until a safe distance and parachute deployment. The capsule will have the same mass as the crewed version.
The mission will be tracked by the team at Sriharikota. If successful, India will be the fourth country, after Russia, United States and China, to master this technology. Gaganyaan 1, the first orbital test flight, is planned to 2024.

About the Rocket
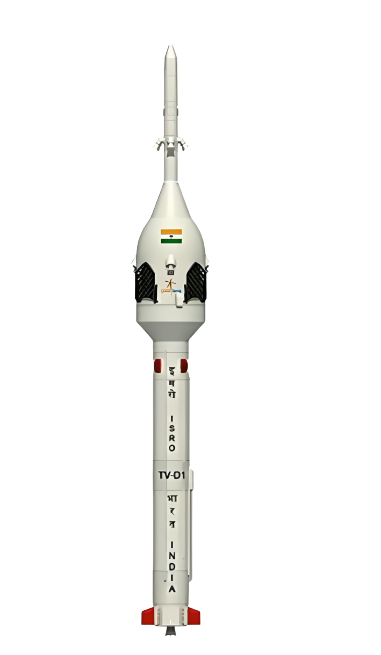
- Specifications
Height - approx 25m
Core Diameter - 2.1 m
Stages - 1st Stage (L40)
Apogee - 11 km
Landing - Splashdown in Bay of Bengal
Sep Motors - Solid Fuel HTPB
About the Payload
Crew Module -
Gaganyaan crew module is a fully autonomous 5.3 t spacecraft designed to carry a 3-member crew to orbit and safely return to the Earth after a mission duration of up to seven days. The crew module is equipped with two parachutes for redundancy, while one parachute is good enough for safe splashdown. The parachutes would reduce the speed of the crew module from over 216 m/s to under 11 m/s at splashdown.
The space capsule will have life support and environmental control systems. It will be equipped with emergency mission abort capabilities and a Crew Escape System (CES) that can be activated during the first stage or second rocket stage burn. The nose of the original version of the orbital vehicle was free for a docking mechanism, but primary entry was evidently through a side hatch secured by explosive bolts. On 7 December 2022, the crew module entered the production stage.
Service module -
Its 2.9 t service module is powered by liquid propellant engines. The crew module is mated to the service module, and together they constitute 8.2 t orbital module.
The Service Module Propulsion System (SMPS) will perform an orbit raising manoeuvre allowing Gaganyaan to reach 400 km in low earth orbit (LEO), then remain docked during a deorbit burn until atmospheric reentry. It will use an unified bipropellant system consisting of MON-3 and Monomethylhydrazine as oxidizer and fuel, having five main engines derived from ISRO's liquid apogee motor with 440 N thrust and sixteen 100 N reaction control system (RCS) thrusters.
The first in a series of tests to qualify a Crew Escape System, which is a critical technology relevant for human spaceflight. The Crew Escape System is an emergency escape measure designed to quickly pull the crew module along with the astronauts to a safe distance from the launch vehicle in the event of a launch abort.

